Working from home was a thing before Covid-19 broke out, but it has turned into the new way of working now that so many companies have been forced to confront this pandemic and its disruptive effects on people’s personal and professional lives.
And while working from home certainly has its benefits, we have to recognize the challenges, as well. Remote working requires new security standards to be adopted, different from those used when all employees are working in one, centralized location. This is especially true for those organizations that need to maintain data security according to the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
How does GDPR affect working from home?
Employees are not only in charge of accomplishing specific assignments during the workday – they are also in charge of handling personal and business data, even when working from home. Regardless of the physical location in which the work can be done, the GDPR requires the same security measures to be applied in order to ensure data security and avoid data breaches.
People who are working remotely are, in some respects, more likely to be exposed to security risks and threats. Let’s take a look at some aspects to keep in mind when talking about remote working: devices, access, and storage.
Devices. Employees working from home may use their personal devices, such as laptops or smartphones, which may not have all of the appropriate technical measures required by the company for workstations physically present in the office. This lack of security could turn into serious vulnerabilities to external threats such as clicking on unfamiliar web links, opening attachments, or visiting unsafe websites. Moreover, employees could be tempted, outside of the office, to use their personal accounts for work (private email, file sharing systems, or storage) because it seems to be more convenient, thereby mixing the organization’s data with their own personal data. The GDPR requires people to be aware of the types of data they handle and the purpose of the processing.
Access and storage. Remote workers may not be aware of the big differences between accessing company data from the office, and accessing that same data from home. The data may be the same, but it loses its integrity when it is handled without the appropriate technical safeguards. Similarly, data could be taken from the secure storage facilities provided by the company and kept in personal storage (such as on a computer screen or a pen drive), where it could be seen or, even worse, erased. It’s just a fact that many employees working from home share their space with other family members or roommates – and they may feel perfectly comfortable, though they are actually putting their work at high risk. The GDPR does not make distinctions between rooms or places or conditions in which data is processed; it simply requires appropriate security against potential risks – whenever and wherever that data may be.
In addition, employees working from home may connect to the internet using personal – or even public – Wi-Fi. Though personal internet connections are likely safer than public, there are still significant security risks in both cases, as the connection is not protected with the same measures that a company would implement in its corporate offices.
How do you keep security when employees work remotely?
As we have learned over the last several months, remote working can help companies to keep their business operating even in the case of emergencies, such as the Covid-19 outbreak. Nevertheless, employees working from home are typically not familiar enough with data security issues to prevent data breaches from exposing sensitive data.
First, employees should be clear on how to handle data, regardless of the location in which they work, and how to guarantee data protection and data privacy. Data must be kept safe when in transit, such as when data is transferred from a company’s server to an employee’s workstation, and when in storage, such as when data is put onto a hard drive.
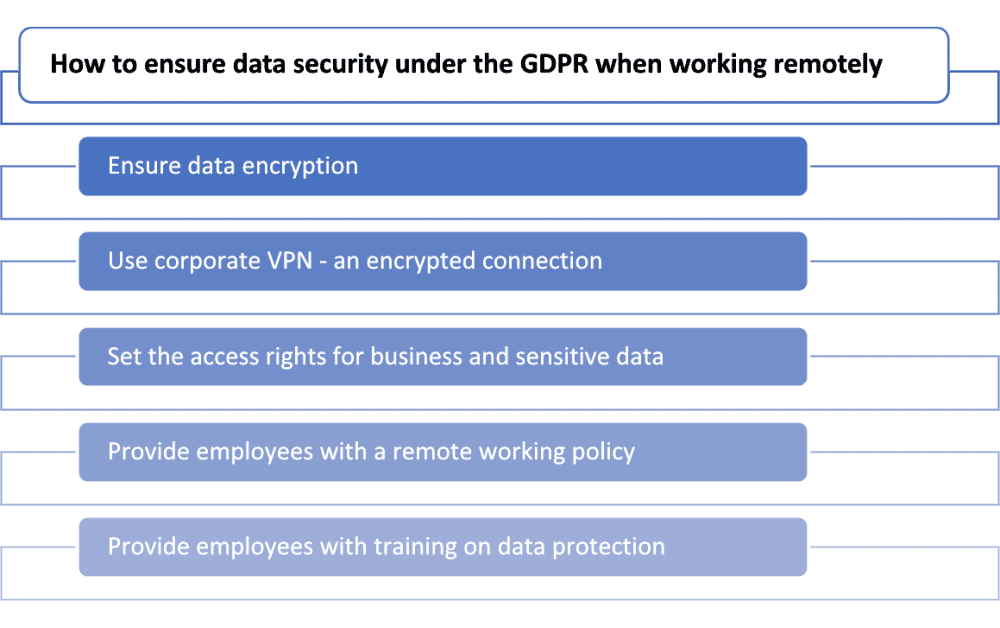
The General Data Protection Regulation requires organizations to adopt security measures, such as encryption, to protect data from inappropriate use. Encryption represents a useful method to keep data safe, especially in the case of a breach – even if stolen or exposed, encrypted data would be illegible and useless anyway. Encryption is easier to adopt when working in a company’s offices, but it can also be implemented in devices and software when working remotely.
Second, access to company data, whether business or sensitive, should be controlled. Employees should have the right to access only that data that is necessary to accomplish their daily tasks. Measures such as “need to know”. “least privilege”, and “segregation of duties” should be in use so that the company’s data is protected from information loss. Moreover, companies should ask their employees to use a corporate Virtual Private Network (VPN), which is an encrypted connection over the internet from a device to a network: in this way, data could be safely transmitted, while preventing access by unauthorized people.
For more information about what steps to take in order to reduce risks related to the processing of personal data and still be compliant with the GDPR when working remotely, take a look at this free webinar: How to make work from home compliant with the GDPR.
Last, but not least, companies should provide their employees with a remote working policy in which rules and tips for remote working are clearly listed. Remote employees should be instructed on how to keep personal information and company data safe, especially when working from home. Moreover, they should be regularly trained about the best practices and guidelines to adopt for data protection. Only in this way, with employees aware of the role they play in keeping data safe (whether working from home or at the office), can a company really ensure GDPR compliance.
Learn more in this article: How cybersecurity solutions can help with GDPR compliance.
The impact of the GDPR on working from home
As we have just seen, the GDPR applies to the company’s employees working in any location, whether in the office or remotely. Organizations must be aware of the security risks associated with new ways of accessing data, such as working from home. This leads to the increasing importance of a remote working policy: to help to protect data (sensitive, personal, or business data) anytime and anywhere.
To have a better idea of all the necessary steps to comply with the EU GDPR when working from home, download this free material: Project checklist for EU GDPR implementation.

 Francesca Lucarini
Francesca Lucarini